In this post, you will learn, how we can retrieve, activate or deactivate Web scoped features on SharePoint site or sub sites, using PnP PowerShell. The Client Side Object Model is used internally for these operations.
Prerequisite:
You need to have PowerShell 3.0 available on a Windows machine. You need to install or import PnP PowerShell packages. You can download the installers or view more documentation on the official site. The installers are available here. Online version installer is preferred for On Premise or Office 365 operations. You can also install all the three installers for testing (SharePoint 2013, 2016, online).
The following operations will be compatible with SharePoint 2013 On Premise and Office 365 versions.
Connect To Site:
Connect to the site, using the snippet, given below. PnP PowerShell code, given below, helps in getting the current context of the site, using the Client Side Object Model (CSOM).
- #Get Current Context Site (Root or subsite)
- $siteurl = "https://abc.sharepoint.com/subsite"
- Connect-SPOnline -Url $siteurl
- $ctx = Get-SPOContext
Since, we are working with the features with Web Scope, the site URL can be the site collection or sub sites available. Once connected, you can carry out any of the operations mentioned below, based on the requirement.
Retrieve Web Scope Features:
The Web scoped features active on the site or sub sites are retrieved in the operation, given below. Get-SPOFeature command is used to get all the features from the site. Since, we are retrieving the Web scoped features, the scope parameter is not required in this operation.
Each and every feature information is retrieved, using for each loop. The display name and definition Id are retrieved from the features. The code snippet given below helps retrieving all the Web scoped features from the site or sub site, specified in the context.
- function RetrieveFeatures(){
- # Get Web Scoped features
- $features = Get-SPOFeature -Scope Web
- Write-Host "Total active features count " $features.Count
- foreach($feature in $features){
- Write-Host "Feature Name : " $feature.DisplayName
- Write-Host "Feature ID : " $feature.DefinitionId
- }
- }
- RetrieveFeatures #Get all web scoped features from site
The feature can be retrieved, using the identity. The identity can be the feature name or Id. The scope parameter is optional. Though, Web is passed as a scope. The following code snippet retrieves the feature, using the feature Id.
- function RetrieveFeature(){
- $features = Get-SPOFeature -Scope Web
- # Check whether FollowingContent feature is active
- $feature = Get-SPOFeature -Identity a7a2793e-67cd-4dc1-9fd0-43f61581207a -Scope Web
- if($feature.DisplayName -ne $null){
- Write-Host $feature.DisplayName " feature is active"
- }
- else{
- Write-Host "Couldn't find info about feature id. Feature is not active"
- }
- }
- RetrieveFeature #Get web scoped feature from site using feature id
Enable Web Scope Feature:
The feature can be activated, using PnP PowerShell script. Enable-SPOFeature command is used to activate the features. Along with the command, the necessary parameter is the identity. The identity is the feature Id. The scope is an optional parameter.
The code snippet, given below, helps in activating the feature at the Web scope.
- function EnableFeature(){
- # Active Mobile View web feature
- Enable-SPOFeature -Identity d95c97f3-e528-4da2-ae9f-32b3535fbb59 -Scope Web
- $feature = Get-SPOFeature -Identity d95c97f3-e528-4da2-ae9f-32b3535fbb59 -Scope Web
- if($feature.DisplayName -ne $null){
- Write-Host $feature.DisplayName " feature is activated"
- }
- else{
- Write-Host "Feature is not activated"
- }
- }
- EnableFeature # Activates Mobile View web feature using feature id
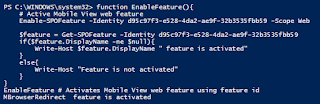
The image, given below, shows the activated feature. The URL is required to access the Web scope feature.
Disable Web Scope Feature:
The feature can be deactivated, using PnP PowerShell script. Disable-SPOFeature command is used to deactivate the features. Along with the command, the necessary parameter is the identity. The identity is the feature Id. The scope is an optional parameter.
The code snippet, given below, helps in deactivating the feature at the Web scope.
- function DisableWebFeature(){
- Disable-SPOFeature -Identity d95c97f3-e528-4da2-ae9f-32b3535fbb59 -Scope Web
- $feature = Get-SPOFeature -Identity d95c97f3-e528-4da2-ae9f-32b3535fbb59 -Scope Web
- if($feature.DisplayName -eq $null){
- Write-Host $feature.DisplayName " feature is deactivated"
- }
- else{
- Write-Host "Feature is still active"
- }
- }
- DisableWebFeature # Deactivates Mobile View web feature using feature id
Note: The operations will be compatible for SharePoint 2013/2016 On Premise / SharePoint online sites.